EDIT: Ninga'd by @Gaarst
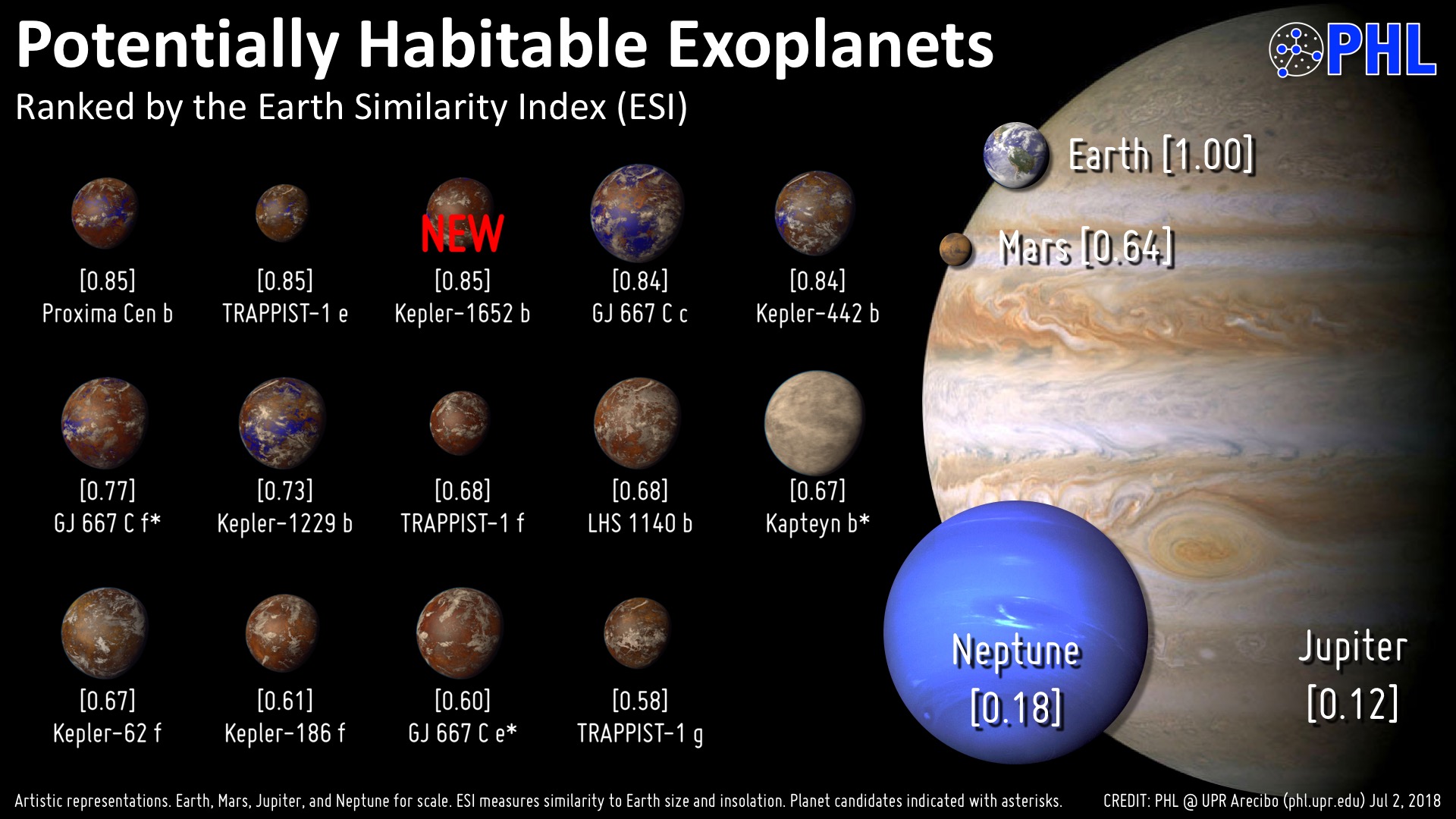
Alright, I'll take a crack at this, ESI is Earth similarity index, and goes from 0.0 (Not even remotely Earthlike) to 1.0 (An exact twin, or as close as you can get to one), TRAPPIST-1d has an ESI of 0.9 or 90% on the scale.
Right Ascension (Taken from google): The distance of a point east of the First Point of Aries, measured along the celestial equator and expressed in hours, minutes, and seconds.
Declination (Also from google): The angular distance of a point north or south of the celestial equator.
Constellation: A group of stars that make a pattern in the sky, like the Big Dipper.
Apparent magnitudes (From good ol' wiki): The apparent magnitude of a celestial object a number that is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth. The brighter an object appears, the lower its magnitude value (i.e. inverse relation). The Sun, at apparent magnitude of −27, is the brightest object in the sky.
Parallax (Google): Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight, and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines.
Distance: Pretty straightforward, for light years, it's 5.878625 trillion miles. For Parsecs, it's 19.173511577 trillion miles.
Mass: The mass of an object in Astronomy is usually comparing one body with the Earth, Jupiter, or the Sun, depending on how massive it is, the same is for Radius, comparing the radius of a planet or star compared to the Earth, Jupiter, or the Sun.
Density (From google): The term density appears in astronomy in many different contexts. In its most generic use the density is the mass per unit volume of an object or region and might have units like kg/m^3 or Mo/pc^3.
Effective temperature (Google): the temperature of an object calculated from the radiation it emits, assuming black-body behavior.
Luminosity (From wiki): In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of energy emitted by a star, galaxy, or other astronomical object per unit time.[1] It is related to the brightness, which is the luminosity of an object in a given spectral region.
Metallicity (From google): In astronomy and physical cosmology, the metallicity or Z is the fraction of mass of a star or other kind of astronomical object that is not in hydrogen (X) or helium (Y).
Age: How old an object is, I believe in astronomy, they measure the age by millions or billions of years.